Preventing Stampedes in India Introduction
- India has witnessed a tragic number of stampedes, with the highest fatalities globally. According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), from 1996 to 2022, over 3,900 stampede incidents have occurred, claiming more than 3,000 lives.
- This alarming data underscores the critical need for effective crowd management strategies to ensure the safety of large gatherings.
What is a Stampede?
- A stampede occurs when a large crowd becomes uncontrollable, leading to impulsive movements that disrupt orderly crowd behavior.
- This often results in injuries or fatalities due to the sudden pressure on individuals as they are crushed or trapped in dense crowds.
Key Causes of Stampedes
- High Crowd Density: Overcrowded spaces create pressure points that make it difficult for people to move freely, increasing the risk of stampedes.
- Lack of Understanding of Crowd Behavior: Without understanding how crowds behave under stress, organizers fail to predict and prevent dangerous situations.
- Inadequate Planning: Poor preparation and lack of clear roles for authorities and organizers can escalate crowd chaos during emergencies.
- Lack of Coordination: Absence of effective communication between organizers, local authorities, and emergency services can lead to confusion, exacerbating the risk of stampedes.
Fatalities in Stampedes
- Traumatic Asphyxia: External pressure on the chest or abdomen prevents breathing, causing fatalities.
- Heart Attacks (Myocardial Infarction): Stress and panic can trigger heart attacks in vulnerable individuals.
- Crushing Injuries: The force of the crowd can cause internal injuries or even death.
- Head and Neck Injuries: Severe injuries to the head or neck can lead to fatalities, even if other injuries are less severe.
Understanding Crowd Management
- Crowd management involves strategic planning, organizing, and monitoring large gatherings to ensure that people can move safely and without incident.
- The goal is to minimize the risks associated with crowd-related events, preventing stampedes and other crowd-related accidents.
Objectives of Crowd Management
- Preventing Accidents: By identifying potential risks in advance, organizers can minimize the chances of accidents and ensure safety.
- Mitigating Risks: A well-prepared crowd management plan reduces the likelihood of harm before, during, and after the event.
- Ensuring Safety: The safety and well-being of everyone involved in large gatherings is the central focus of crowd management.
NDMA Guidelines for Effective Crowd Management
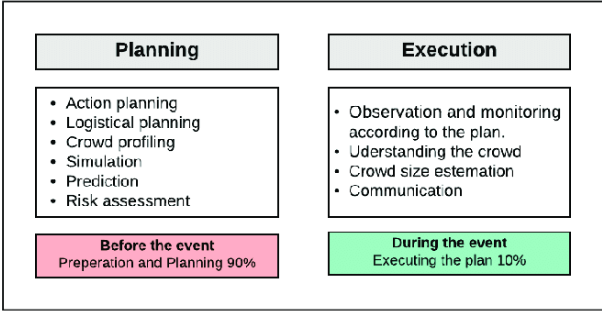
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has developed comprehensive guidelines aimed at reducing stampedes and ensuring effective crowd management. These guidelines focus on capacity planning, crowd control, and risk analysis, providing a structured approach for event organizers and authorities.
- Capacity Planning:
- Visitor Monitoring: Implementing systems to track and monitor the number of visitors at key staging points can prevent overcrowding and ensure the venue stays within safe limits.
- Staging Points: Organizers must establish clear entry and exit points, where people can be monitored and controlled. These points should also have essential facilities such as resting areas, food, and water stations to support crowd welfare.
- Multiple Routes: Providing various entry and exit paths will help distribute the crowd evenly, reducing congestion and improving crowd flow.
- Crowd Control:
- Controlling Inflow: Regulating the number of people entering the venue ensures the crowd remains manageable and within safe limits.
- Regulating Movement: Ensuring that people can move freely within the venue prevents bottlenecks that could lead to dangerous situations.
- Controlling Outflow: Ensuring a structured and safe exit strategy is essential to prevent a stampede during crowd dispersal after the event.
- Hazard, Risk, and Vulnerability Analysis (HRVA):
- Identifying Threats and Causes: Organizers should assess the venue and past incidents to identify potential risks, such as overcrowding or infrastructure failure.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying risks, planners must assess their potential impact and likelihood, allowing them to prepare better for any possible emergencies.
- Simulating Scenarios: Pre-event simulations can help planners predict how crowds might behave in different emergency situations and prepare appropriate responses.
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA): FMEA helps assess potential hazards by evaluating their severity, frequency, and detectability. Each hazard is rated to determine its Risk Priority Number (RPN), helping planners prioritize which risks require immediate attention.
- Severity: The potential damage caused by the hazard.
- Frequency of Occurrence: How often the hazard is likely to happen.
- Difficulty of Detection: How easily the hazard can be identified in time to prevent harm.
- Developing a Course of Action:
- Resource Assessment: Planners should assess the resources needed to mitigate identified risks, comparing them with what is available. This ensures they have the necessary tools and manpower to respond to emergencies.
Way Forward
- Implementing a Stampede Risk-Reduction Framework: India needs a multi-disciplinary approach that involves collaboration between event organizers, local authorities, law enforcement, and emergency services. This framework should be designed to anticipate and address risks before they escalate.
- Improving Venue Design: Better venue design can alleviate crowd pressure points and prevent congestion. Planning venues that account for safe movement and crowd behavior will help reduce the chances of a stampede.
- Real-time Surveillance: Implementing live surveillance systems can help organizers monitor crowd behavior and density, detecting potential risks in real-time. This allows for quick interventions to avoid dangerous situations.
- Clear Communication and Coordination: Effective communication between event organizers, local authorities, and law enforcement is essential for managing emergencies. A clear chain of command and decision-making process will help ensure a coordinated response when needed.
- Prioritizing Emergency Preparedness: Emergency preparedness is crucial in preventing fatalities in the event of a stampede. This includes the deployment of trained personnel, emergency medical services, and clear protocols for managing crises during mass gatherings.















