Fluvial Desert Landforms
Running water plays a significant role in shaping landscapes, particularly in semi-arid regions that experience moderate rainfall.
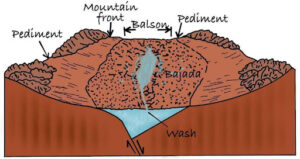
- Washes/Wadis: These are valley-like ravines, often characterized by interlocking spurs.
- Badlands: When a surface is heavily dissected by numerous wadis, it results in a distinctive topography known as Badlands.
- Example: The Chambal Badlands in India.
- Mesas and Buttes: In arid plateaus, when a resistant horizontal layer is eroded by wind and water, it forms mesas and buttes.
- Mesas: Flat-topped, steep-sided landforms separated from the main plateau.
- Buttes: Smaller versions of mesas.
- Bolsons: These are intermontane basins found in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Playas: Temporary lakes that form in the center of bolsons where water accumulates.
- Example: Lake Lop Nor in the Tarim Basin, northwest China.
- Pediments: Broad, gently sloping rock-cut surfaces located between a mountain front and the adjacent bajada.
- Bajada: A gently sloping depositional plain that lies between pediments and playas.
- Formed by the merging of several alluvial fans.
|
UPSC Articles |
|
| UPSC Interview Marks | |
| UPSC Selection Process | |














