Extrusive Volcanic Landforms
These landforms are created when lava solidifies on the Earth’s surface, accompanied by the accumulation of pyroclastic materials such as volcanic ash, dust, and debris.
Landforms of Central Eruption
| Landform | Characteristic Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cinder Cones | Small mounds formed by the accumulation of volcanic dust, ashes, and pyroclastic materials around the vent. | Cones of Mt. Jorullo in Mexico. |
| Shield Volcano | Created by successive layers of lava accumulating around the vent, resulting in a broad, gently sloping structure. | Mauna Loa in Hawaii, the largest shield volcano. |
| Composite/Strato Volcano | Tall, steep-sided, and conical volcanoes with stratified layers of lava and ash. | Fujiyama, Cotopaxi, and Vesuvius. |
| Crater | Funnel-shaped or basin-like depressions at a volcano’s summit. Extinct craters may fill with water, forming crater lakes. | Crater Lake in Oregon, Lake Toba in Indonesia. |
| Caldera | A large, shallow cavity often larger than a typical crater, formed by volcanic activity. | Caldera on Mt. Krakatoa. |
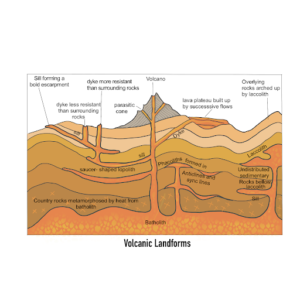
Intrusive Volcanic Landforms
These landforms develop when magma solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface, forming various igneous rock structures.
| Intrusive Landform | Characteristic Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Dyke | A vertical or steeply inclined sheet of igneous rock cutting through existing rock formations. | Dykes in the Chotanagpur Plateau. |
| Sill | Horizontal sheets of igneous rock formed between sedimentary rock layers. | Tabular quartz trachyte near Engineer Mountain, Colorado. |
| Laccolith | A dome-shaped igneous rock mass with a flat base and an arched upper surface. | Mt. Holmes in Yellowstone National Park, USA. |
| Lopolith | A large, saucer-shaped igneous rock structure. | Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa. |
| Phacolith | Lens-shaped igneous rock formations found in folds of strata. | Found in the foothills of the Himalayas and Alps. |
| Batholith | Massive dome-shaped formations of igneous rock, extending deep below the surface. | Wicklow Mountains, Ireland. |
Impacts of Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions have a range of positive and negative consequences:
Positive Impacts
- Fertile Soil: Lava breakdown enriches soil fertility, aiding agriculture.
- Geothermal Energy: Potential for harnessing renewable energy sources.
- Tourism Development: Unique landscapes and geological features attract visitors.
Negative Impacts
- Loss of Life and Property: Volcanic activity can devastate human settlements.
- Lahars: Mudflows result when volcanic ash mixes with rainwater or snowmelt, causing destructive flows.
- Climate Change: Volcanic eruptions release gases and ash into the atmosphere, potentially altering climate patterns.
|
||||||||||