India’s Deep-Tech Startup Ecosystem Introduction
- Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal’s recent remarks on India’s startup ecosystem highlighted a crucial gap: while the country is making strides in the tech sector, it lags behind China in the development and adoption of advanced technologies.
- This raises the question—can India bridge this gap? The answer lies in fostering and nurturing deep-tech startups, which are poised to revolutionize sectors across the nation.

What Are Deep-Tech Startups?
- Deep-tech startups are innovative ventures that focus on complex, high-tech fields such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep Learning, Robotics, Semiconductors, Biotechnology, Space Technology, and Electric Vehicles (EVs).
- These startups aim to address multifaceted problems and deliver transformative solutions with the potential to significantly impact industries and improve lives on a global scale.
The Significance of Deep-Tech Startups for India
- Driving Innovation and Transformative Change: Deep-tech startups are at the forefront of groundbreaking innovations. Just as Alexander Fleming’s discovery of Penicillin in 1928 led to the creation of antibiotics, deep-tech innovations drive the next wave of technological breakthroughs. For example, GenAI has the potential to revolutionize sectors ranging from healthcare to education and finance.
- Economic and Industrial Growth: India’s GDP can see a significant boost through deep-tech innovations. According to experts, deep-tech startups, particularly in AI and Semiconductors, could add $1 trillion to India’s economy by 2030. These technologies are central to Industrial Revolution 4.0 and are integral to India’s future economic trajectory. Former NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant underscores that these innovations will be pivotal for India’s aspirations to become a developed economy by 2047.
- Strategic Importance for National Security and Self-Reliance: Deep-tech innovations also play a critical role in enhancing India’s self-reliance (Atmanirbharta). By advancing technologies in defence, energy, and healthcare, India can reduce its dependence on foreign technologies and secure its national interests. Take, for example, China’s DeepSeek AI—a strategic development aimed at achieving technological independence amid US-led restrictions on advanced semiconductor exports.
- Solving Societal Challenges: Indian-centric deep technologies can provide tailored solutions to local problems. Innovations in affordable healthcare, sustainable energy, language-based AI, and bridging the North-South divide can drastically improve the lives of millions. For example, AI-driven diagnostics can help in affordable rural healthcare, while sustainable energy solutions can address power shortages across remote areas.
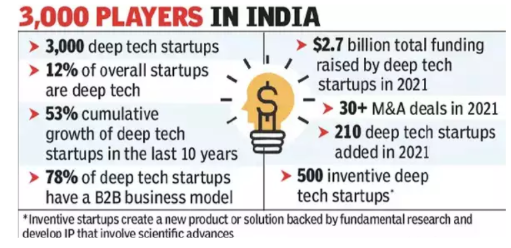
Challenges Hindering Deep-Tech Startups in India
- Long Gestation Period: Deep-tech startups typically require longer timelines for R&D and product commercialization, often far exceeding the venture capital timelines in India. This long-term investment challenge, coupled with obstacles like Angel Tax (now scrapped), delays innovation in the deep-tech sector.
- India’s Talent Paradox: Despite producing millions of engineers annually, only a fraction specialize in cutting-edge fields like AI and robotics. Moreover, the brain drain continues as talented professionals migrate to countries like the USA, where many drive innovations at companies like Tesla, NVIDIA, and startups in Silicon Valley. This talent shortage hinders India’s deep-tech potential.
- Low R&D Funding and Investment: India’s R&D expenditure is significantly low, less than 1% of its GDP, compared to USA, UK, Germany, and China which spend over 3% of their GDP on research. In contrast, while China’s ‘Made in China 2025’ initiative invested over $800 billion into strategic sectors, India’s $160 billion technological investment from 2014-2024 remains insufficient. The funding gap severely restricts deep-tech startups in India from scaling innovative solutions.
- Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles: The IPR protection process in India is complex and time-consuming, and regulatory uncertainties in sectors like genomics, drones, and AI hamper the development of deep-tech startups. This unpredictability discourages investors and entrepreneurs from pursuing high-risk innovations.
- Global Competition: China and the USA dominate the deep-tech space, with China leading in 57 out of 64 critical technologies. According to a WIPO report, China filed over 38,000 generative AI patents between 2014-2023. India’s competitive edge in global tech markets remains underdeveloped in comparison to these technological giants.
- Stagnation in Startup Ecosystem: While India has become the third-largest startup ecosystem, the majority of startups are focused on quick commerce and consumer tech, rather than groundbreaking deep-tech innovations. Startups like OpenAI, Blue Origin, and DeepMind are not yet common in India, limiting the potential for long-term technological breakthroughs.
- Innovation Ecosystem Deficits: India ranks 39th in the Global Innovation Index 2024, with a significant gap in fostering original research and innovation. No Indian universities or research institutes are currently among the global leaders in pioneering research, creating a challenge for deep-tech startups reliant on strong academic backing.
- Commercialization Bottlenecks: Indian deep-tech startups struggle to transition from prototype to market-ready product due to long R&D cycles, lack of industry-academia collaboration, and inadequate regulatory sandboxes. These bottlenecks delay the commercialization of innovations, reducing the pace of technological adoption.
Government Initiatives Supporting Deep-Tech Startups
- Policy Reforms in High-Tech Sectors: The Indian government has launched various initiatives to promote innovation in high-tech sectors, such as the Indian Space Policy 2023, liberalized Drone Rules 2024, and Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy 2023, which aim to boost self-reliance and innovation in sectors like space and defense.
- India Semiconductor Mission: The government allocated ₹76,000 crore for building semiconductor FAB capacity and a design ecosystem to reduce India’s dependency on foreign semiconductor imports and foster deep-tech growth.
- IndiaAI Mission: In 2024, India approved ₹10,000 crore for the IndiaAI Mission, aimed at building a comprehensive AI ecosystem to foster research and development in AI technologies.
- National Supercomputing Mission: India is developing a network of 70 high-performance computer facilities with a 45 PF (Petaflop) cumulative capacity to support deep-tech R&D and AI-powered innovation.
- National Quantum Mission: India’s National Quantum Mission seeks to position India among the top six countries globally involved in quantum technologies, enhancing capabilities in AI, cryptography, and material sciences.
- Deep Tech Fund & Space Tech Fund: To address the funding gaps, the government has introduced a ₹10,000 crore Deep Tech Fund and a ₹1,000 crore space tech venture capital fund, aimed at catalyzing deep-tech innovation and bridging critical funding gaps.
- Innovation Ecosystem Initiatives: Programs like the Atal Innovation Mission, NIDHI-PRAYAS, and T-Hub are designed to foster innovation at the early stages of startup development and provide necessary support for young entrepreneurs in deep-tech.
- Pockets of Success in Deep-Tech: India has seen success in specific deep-tech domains such as space tech (e.g., Skyroot, Agnikul), robotics (e.g., Addverb, CynLR), and EVs (e.g., Ola, Ather). These success stories, supported by government initiatives, indicate potential for growth. In 2024, India’s 4,000 deep-tech startups raised $1.6 billion, a 78% increase year-on-year.
Way Forward
- Increase R&D Investments India should boost R&D investments to at least 2% of its GDP to match global leaders like the USA, China, and France, who have dedicated billions to deep-tech sectors.
- Increase & Patient Capital Attracting long-term venture capital and establishing government-backed funds will be crucial for enabling deep-tech startups to mature and scale successfully over longer periods.
- Strengthen Industry-Academia Collaboration India must foster closer collaboration between academic institutions (e.g., IITs, IISc) and deep-tech startups. Drawing inspiration from DARPA and NASA, India can encourage innovative, high-risk projects.
- Education Sector Reforms India’s education system must focus on cutting-edge research and promote innovation from early stages, preparing students for deep-tech entrepreneurship.
- IPR Ecosystem Reforms Simplifying IPR processes and speeding up patent approvals will be vital for promoting deep-tech innovation in India.
- Global Integration India should foster international collaborations to access global markets and R&D. Participation in global standards bodies and tech consortia will help position India as a hub for frontier technologies.
- Develop Specialized Talent India needs to focus on training and upskilling professionals in deep-tech domains while also attracting global talent to work on cutting-edge innovations in India.















