UPSC GS 1
World Drought Atlas
- News: Around 75 per cent of the population will be affected by drought by 2050, according to the World Drought Atlas.
- About World Drought Atlas:
-
- The World Drought Atlas was launched by the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in partnership with the European Commission Joint Research Centre.
- It explores the increasing risks of drought caused by human activities and highlights the impacts in five critical areas: water supply, agriculture, hydropower, inland navigation, and ecosystems.

- Key Features:
- Case Studies:
- The atlas includes 21 case studies from various parts of the world, demonstrating that no country—regardless of size, economic status, or geographic location—is exempt from drought risks.
- It emphasizes that all nations can enhance their preparedness for drought.
- Practical Solutions:
- The document offers concrete strategies to manage, mitigate, and adapt to systemic drought risks.
- It also highlights the co-benefits of these actions across multiple sectors and presents examples of best practices from different regions.
- Categories of Measures:
- Governance:
- Implementation of early warning systems for better preparedness.
- Introduction of microinsurance schemes tailored for smallholder farmers.
- Adoption of water usage pricing mechanisms to promote efficient use.
- Land-Use Management:
- Restoration of degraded land to improve resilience.
- Promotion of agroforestry practices to enhance land productivity and reduce risks.
- Water Supply and Usage:
- Reuse of treated wastewater to conserve fresh water.
- Managed groundwater recharge for sustainable water availability.
- Conservation practices to optimize water use.
- Purpose and Benefits:
-
- The atlas provides actionable pathways to address drought risks, highlighting the importance of integrating these measures for long-term sustainability.
- It underscores the dual benefits these actions bring to various sectors while fostering resilience against climate change impacts.
Read also: Child Marriage in India: Issues & Solutions | UPSC Prep
Homo Juluensis
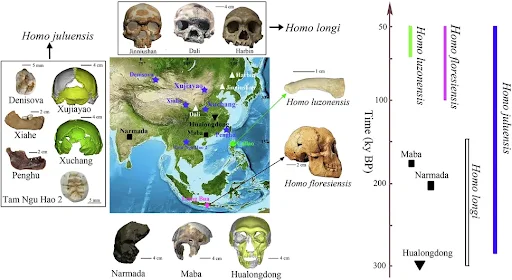
- News: Researchers have identified a new species of ancient humans, which they have named Homo juluensis, meaning “big head,” based partly on a very large skull found in China.
- About Homo Juluensis:
-
- Homo juluensis is a newly identified ancient human species, characterized by exceptionally large skulls.
- Often referred to as the “big head people,” this species lived approximately 300,000 years ago and persisted in small groups across eastern Asia before their extinction around 50,000 years ago.
- This species includes enigmatic groups such as the Denisovans, whose histories remain under investigation.
Neanderthals
|
- Key Characteristics:
-
- Fossil remains, primarily of facial and jawbones, reveal dental features akin to those of Neanderthals.
- Preliminary measurements suggest that the braincases of Homo juluensis were up to 30% larger than those of modern Homo sapiens.
- They were skilled hunters, targeting wild horses in small groups, and utilized stone tools.
- Evidence indicates they may have processed animal hides as part of their survival strategies.
Tikhir Tribe
- News: The Tikhir tribe recently organized a Log Drum Pulling ceremony at the ongoing 25th Hornbill Festival in Kisama Heritage Village, Kohima.
- Location: The Tikhir tribe is one of the indigenous Naga tribes, primarily residing in Nagaland, India, with some members also living across the border in Myanmar.
- Language: They speak Naga Yimchungru, a language belonging to the Tibeto-Burman family, like most Naga languages.

- Historical Practices: Historically, the Tikhirs were headhunters, where a man’s social status was often tied to the number of enemies he had defeated.
- Livelihood: Their primary means of sustenance are agriculture and hunting.
- Challenges: Being a smaller tribe, the Tikhirs often face harassment from larger neighboring tribes.
- Religion: With the arrival of Christian missionaries in Nagaland, most Tikhirs converted to Christianity.
- Cultural Practices: Many continue to integrate elements of traditional folk religion with their Christian beliefs.
- Tsonglaknyi: This is their primary festival, celebrated annually from October 9th to 12th. It is a festival of shield sanctification, reflecting their historical and cultural identity.
UPSC GS 2
SheSTEM 2024
- News: Atal Innovation Mission under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
- About SheSTEM 2024:
- Overview:
- SheSTEM is an annual event organized by the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) in collaboration with the Office of Science and Innovation at the Embassy of Sweden.
- It highlights and celebrates the contributions of women in STEM fields while inspiring young minds to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
- Focus of SheSTEM 2024:
- The event invited students from grades 6–12 across India to participate in a challenge centered on Battery Technology and Energy Storage (BEST) systems.
- This challenge was part of the India-Nordic BEST project, emphasizing sustainability and the advancement of energy solutions.
- Participants were required to present their innovative concepts or prototypes related to energy storage and sustainability in a two-minute video.
- The competition received over 1,000 entries, showcasing the creativity and problem-solving capabilities of India’s youth.
- Objective: SheSTEM 2024 served as a platform to encourage students to engage with critical STEM issues and contribute to global sustainability goals.
UPSC GS 3
Nano Bubble Technology
- News: Union Minister of State for Forest, Environment and Climate Change has launched ‘Nano Bubble Technology’ for cleaning and purifying water of National Zoological Park, Delhi.
- Definition and Size:
- Nanobubbles are microscopic bubbles ranging in size from 70 to 120 nanometers, which is about 2,500 times smaller than a single grain of salt.
- They can be formed using any gas and can be injected into any liquid.
- Applications:
- Due to their distinctive physical and chemical properties, nanobubbles are highly effective and superior to traditional aeration techniques.
- They are widely utilized in water treatment, agriculture, aquaculture, food processing, and various industrial sectors.

- Properties of Nanobubbles:
- Large Surface Area:
- Their high surface area-to-volume ratio enables extensive gas-to-water interaction.
- The small size and high buoyancy allow them to stay suspended in water, ensuring efficient gas transfer between the gas and liquid phases.
- Brownian Motion:
- Nanobubbles remain in water for extended periods due to their motion, ensuring homogenous oxygen distribution throughout the water body.
- This property helps maintain dissolved oxygen levels over a long duration.
- High Oxygen Transfer Efficiency:
- Nanobubbles achieve an oxygen transfer efficiency of approximately 90% due to their vast surface area and sustained motion.
- Surface Charge:
- They possess a strong negative surface charge, enhancing their separation efficiency during flotation processes.
- This property enables them to float more suspended matter than traditional methods, especially in wastewater, oil, and gas operations.
- Benefits of Nanobubbles:
-
- Enhanced Water Treatment: Nanobubbles are highly effective at eliminating organic pollutants, bacteria, and other contaminants from water.
- Efficient Cleaning: They penetrate surface pores and crevices, delivering a thorough cleaning and effectively removing stubborn dirt and grime.
- Boosted Agriculture and Aquaculture: Providing oxygen nanobubbles to plants and aquatic organisms promotes growth, health, and resilience. Nanobubbles also improve nutrient absorption, reduce reliance on pesticides and chemicals, and enhance crop yields.
- Improved Oil and Gas Recovery: Nanobubbles enhance fluid flow efficiency in oil and gas recovery processes. They minimize the need for chemicals, making operations more efficient.
- Better Skin and Hair Health: Nanobubbles aid in the absorption of skincare products, contributing to healthier skin and hair.
Trouessartia Thalassina and Proterothrix Sibillae
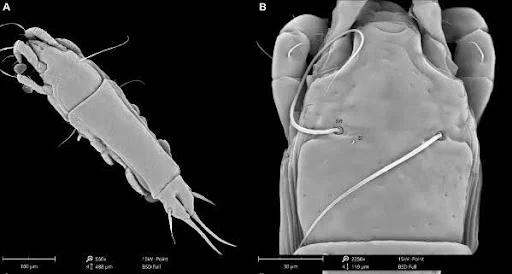
- News: Researchers uncovered two new species of feather mites on flycatchers in Meghalaya, Trouessartia thalassina and Proterothrix sibillae, revealing new insights into India’s rich biodiversity.
- Host Birds: The mites were identified on two bird species native to the East Khasi Hills district of Meghalaya:
-
- Trouessartia thalassina was found on the Verditer Flycatcher (Eumyias thalassinus).
- Proterothrix sibillae was identified on the Small Niltava (Niltava macgrigoriae).
- Distinctive Features:
- Trouessartia thalassina:
- Notable for its semi-ovate terminal lamellae and lanceolate setae in males.
- Females exhibit unique non-sclerotized lacunae.
- Proterothrix sibillae:
- Belongs to the wolffi species group.
- Distinguished by its larger size, circular lacunae on the prodorsal shield, and unique male genital structures.
- Naming Significance:
- Trouessartia thalassina is named after the Verditer Flycatcher, whose striking sea-green plumage inspired the Latin term thalassina, meaning “sea-green.”
- Proterothrix sibillae is named after Honors Maria Sibylla Merian, a renowned German naturalist celebrated for her groundbreaking work in insect taxonomy and her detailed scientific illustrations.
- What Are Feather Mites?
-
- Feather mites are microscopic arachnids that live on bird feathers, feeding on oils, skin flakes, and organic debris.
- They typically form a symbiotic relationship with birds, aiding in maintaining feather cleanliness and health.
- Under stress or unfavorable conditions, they can become parasitic, leading to irritation or feather damage.
- Found worldwide, feather mites are commonly transferred between birds through close contact, especially during nesting periods.
See more: The Gig Economy in India: Growth, Challenges & Insights | UPSC
Gharcholas
- News: Gujarat’s ‘Gharcholas’ sarees have recently been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, adding to the rich heritage of the state.
- Other Names: Known as Ghatchola or Gharcholu, these sarees showcase Gujarat’s finest Bandhani craftsmanship.
- Traditional Significance:
- These sarees have been an integral part of Gujarati weddings for generations.
- The term ‘Gharchola’ translates to ‘Outfit for Home,’ symbolizing a bride’s transition into her new family.

- Features:
- Fabric and Weaving:Crafted on cotton or silk fabric, featuring large checkered patterns woven with silk and zari threads. The checkered design is further enhanced using the Bandhani (tie-and-dye) technique.
- Motifs and Patterns: Each square within the checks is adorned with golden motifs like peacocks, lotus, human figures, and floral designs. Patterns often include symbols of fertility and prosperity, such as the kalash and paan.
- Color Palette: Traditionally crafted in auspicious colors like red, maroon, green, and yellow, which hold cultural significance in Hindu rituals.
- Variants: A saree with 12 squares is called Bar Bagh, while one with 52 squares is referred to as Bavan Bagh.
- Modern Innovations: Contemporary artisans are incorporating modern designs and techniques, blending traditional aesthetics with current trends.
- Craftsmanship: Gharcholas are produced by generational clusters of artisans in Gujarat, preserving the intricate craft through centuries of heritage.
- Geographical Indication: This is the 27th GI tag awarded to Gujarat, underscoring the state’s rich cultural and artisanal legacy.

